2. The Lipid Nature of Biological Membranes.
Lipids make up the bulk of biological membranes, and it's reasonable to suppose their
large numbers greatly influence membrane structure and function. Indeed, it's not too
far-fetched to say membrane lipids and their interactions "create" biological
membranes. How do such small molecules exert such a large role? To answer this question we
need to examine the structure of lipids themselves.
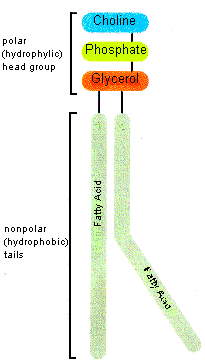 Most
cellular lipids are derived chemically from the three-carbon alcohol, glycerol, through
covalent linkages with up to three fatty acids. Specifically, a fatty acid may form an ester
with each of glycerol's three alcohol residues, and the resulting lipids are called glycerides
All membrane glycerides have fatty acid (hydrocarbon or acyl) residues attached
to two adjacent glycerol carbons and a polar, often charged, residue linked covalently
with the third carbon, and are called diacyl glycerides or simply diglycerides.
Diglycerides containing phosphate as part of the polar residue are called, not
surprisingly, phospholipid. Another major plasma membrane lipid is cholesterol. Different
structural representations of these two membrane lipids are presented on the facing page.
Note in particular, that both types of molecules consist of regions that are hydrophilic,
or water-loving, and hydrophobic, or water-hating.
Most
cellular lipids are derived chemically from the three-carbon alcohol, glycerol, through
covalent linkages with up to three fatty acids. Specifically, a fatty acid may form an ester
with each of glycerol's three alcohol residues, and the resulting lipids are called glycerides
All membrane glycerides have fatty acid (hydrocarbon or acyl) residues attached
to two adjacent glycerol carbons and a polar, often charged, residue linked covalently
with the third carbon, and are called diacyl glycerides or simply diglycerides.
Diglycerides containing phosphate as part of the polar residue are called, not
surprisingly, phospholipid. Another major plasma membrane lipid is cholesterol. Different
structural representations of these two membrane lipids are presented on the facing page.
Note in particular, that both types of molecules consist of regions that are hydrophilic,
or water-loving, and hydrophobic, or water-hating.
 This schizophrenic nature of
membrane lipids seems to be no accident! Scroll through the Table of Membrane Lipids
on the next page and note all of the more common forms share this important feature: all
membrane lipids have a hydrophobic region as well as a hydrophilic one. The long
hydrocarbon chains of the fatty acids (or the fatty-acid like residues) projecting to the
left of each lipid will not spontaneously interact with dipolar water molecules (or
readily dissolve in aqueous solutions). Conversely, the different residues projecting to
the right of each lipid are all polar and will readily interact with water. More
technically, membrane lipids are called amphipathic molecules, because they possess
distinct regions with such different affinities for oil and for water. Even the very
hydrophobic and insoluble cholesterol is slightly amphipathic, by virtue of its single
alcohol residue.
This schizophrenic nature of
membrane lipids seems to be no accident! Scroll through the Table of Membrane Lipids
on the next page and note all of the more common forms share this important feature: all
membrane lipids have a hydrophobic region as well as a hydrophilic one. The long
hydrocarbon chains of the fatty acids (or the fatty-acid like residues) projecting to the
left of each lipid will not spontaneously interact with dipolar water molecules (or
readily dissolve in aqueous solutions). Conversely, the different residues projecting to
the right of each lipid are all polar and will readily interact with water. More
technically, membrane lipids are called amphipathic molecules, because they possess
distinct regions with such different affinities for oil and for water. Even the very
hydrophobic and insoluble cholesterol is slightly amphipathic, by virtue of its single
alcohol residue.
 The
amphipathic nature of membrane lipids contrasts strikingly with the neutral triglycerides and cholesterol esters which
are more abundant in our bodies than their amphipathic relatives.
The
amphipathic nature of membrane lipids contrasts strikingly with the neutral triglycerides and cholesterol esters which
are more abundant in our bodies than their amphipathic relatives.
How do you think these amphipathic molecules would behave if their concentrations were
increased in an aqueous environment? in an organic solvent? at the interface between an
aqueous and an organic solvent? Go on to the next
page to consider the formation of lipid structures called micelles.
 Most
cellular lipids are derived chemically from the three-carbon alcohol, glycerol, through
covalent linkages with up to three fatty acids. Specifically, a fatty acid may form an ester
with each of glycerol's three alcohol residues, and the resulting lipids are called glycerides
All membrane glycerides have fatty acid (hydrocarbon or acyl) residues attached
to two adjacent glycerol carbons and a polar, often charged, residue linked covalently
with the third carbon, and are called diacyl glycerides or simply diglycerides.
Diglycerides containing phosphate as part of the polar residue are called, not
surprisingly, phospholipid. Another major plasma membrane lipid is cholesterol. Different
structural representations of these two membrane lipids are presented on the facing page.
Note in particular, that both types of molecules consist of regions that are hydrophilic,
or water-loving, and hydrophobic, or water-hating.
Most
cellular lipids are derived chemically from the three-carbon alcohol, glycerol, through
covalent linkages with up to three fatty acids. Specifically, a fatty acid may form an ester
with each of glycerol's three alcohol residues, and the resulting lipids are called glycerides
All membrane glycerides have fatty acid (hydrocarbon or acyl) residues attached
to two adjacent glycerol carbons and a polar, often charged, residue linked covalently
with the third carbon, and are called diacyl glycerides or simply diglycerides.
Diglycerides containing phosphate as part of the polar residue are called, not
surprisingly, phospholipid. Another major plasma membrane lipid is cholesterol. Different
structural representations of these two membrane lipids are presented on the facing page.
Note in particular, that both types of molecules consist of regions that are hydrophilic,
or water-loving, and hydrophobic, or water-hating.  This schizophrenic nature of
membrane lipids seems to be no accident! Scroll through the Table of Membrane Lipids
on the next page and note all of the more common forms share this important feature: all
membrane lipids have a hydrophobic region as well as a hydrophilic one. The long
hydrocarbon chains of the fatty acids (or the fatty-acid like residues) projecting to the
left of each lipid will not spontaneously interact with dipolar water molecules (or
readily dissolve in aqueous solutions). Conversely, the different residues projecting to
the right of each lipid are all polar and will readily interact with water. More
technically, membrane lipids are called amphipathic molecules, because they possess
distinct regions with such different affinities for oil and for water. Even the very
hydrophobic and insoluble cholesterol is slightly amphipathic, by virtue of its single
alcohol residue.
This schizophrenic nature of
membrane lipids seems to be no accident! Scroll through the Table of Membrane Lipids
on the next page and note all of the more common forms share this important feature: all
membrane lipids have a hydrophobic region as well as a hydrophilic one. The long
hydrocarbon chains of the fatty acids (or the fatty-acid like residues) projecting to the
left of each lipid will not spontaneously interact with dipolar water molecules (or
readily dissolve in aqueous solutions). Conversely, the different residues projecting to
the right of each lipid are all polar and will readily interact with water. More
technically, membrane lipids are called amphipathic molecules, because they possess
distinct regions with such different affinities for oil and for water. Even the very
hydrophobic and insoluble cholesterol is slightly amphipathic, by virtue of its single
alcohol residue.