Preface | Introduction to Problem Solving | Problem Sets | Acknowledgments
|
B.4. Ca2+ Transport <<Previous Problem Next Problem>> |
PPrint PDF |
(32pts) In addition to the Na+ and K+ pump,
the plasma membranes of many animal cells contain a Ca+ pump that helps
maintain cytoplasmic levels of Ca+ (100 nM) four orders of
magnitude lower than that present in the extracellular environment
(1 mM). It's possible to study this pump using inside-out
vesicles (ISO microsomes) that have been prepared from plasma membranes
of erythrocyte ghosts or the homogenates of other cell preparations.
In the following experiment, an aliquot of ISO microsomes containing 2.0
mg protein was suspended in 1 ml (final vol) of a test medium containing
4 mM Mg2+-ATP and 0.12 M KCl (at pH 7.4), and the hydrolysis
of ATP was measured over time. After 1 min, 2.0 mMol of Ca2+
was added to the reaction mixture; 2 min later a Ca2+ ionophore
(A23187) was added to the mixture. None of the additions changed
the final volume of the reaction mixture. The additions occurred at
the times indicated by arrows.
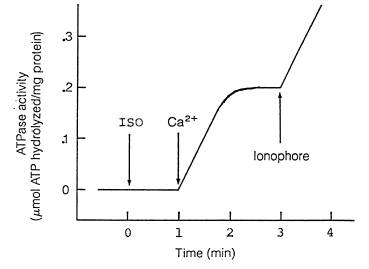 |
Consider these data and answer all the following questions.
All calculations must be shown to receive full credit, your reasoning
must be explicit, and your explanations detailed.
A. (4pts) Why must ISO (in contrast to right-side-out) microsomes
be used to study this particular calcium pump?
B. (4 pts) What is the specific activity of the pump ATPase, expressed
in micromoles of ATP hydrolyzed per mg protein per min?
C. (7 pts) Why does ATP hydrolysis increase rapidly and then reach
a plateau, following the addition of Ca2+?
D. (6 pts) How does the addition of A23187 stimulate ATPase activity?
Would you expect a second plateau? Why or why not?
E. (5 pts) Propose a test of your hypothesis for either question C. or
D. and indicate clearly what the results would show.
F. (6 pts) How could you determine which membrane protein is the Ca2+
pump and estimate its molecular weight? (Note: some methods are
better than others, involving fewer assumptions.)